Popular in your industry





























































Related Searches:









































































































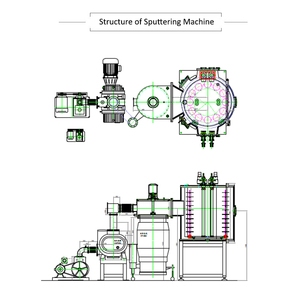













Top categories
About physical vapor deposition
Physical vapor deposition (PVD) is a vacuum coating process that produces a thin film on an object by heating the material and evaporating or sputtering it onto the object's surface. PVD coatings can provide various functional and decorative properties to materials, making them widely used in industries ranging from aerospace to electronics. The most common metals used in PVD processes include titanium, aluminum, and chromium, with applications in producing wear-resistant coatings, decorative finishes, and improving the durability of cutting tools. The PVD coating process can be categorized into evaporation, sputter deposition, and electron beam vapor deposition, each with its advantages and applications.
Types of Physical Vapor Deposition
Vapor deposition can be carried out in a vacuum environment with a pressure of 10-2 Pa or lower. There are three main methods for vapor deposition: vacuum evaporation, sputter deposition, and ion plating. The physical vapor deposition coating is a process of depositing a thin film on a substrate by evaporating or sputtering a material in a vacuum environment. Vacuum evaporation involves the material to be deposited being heated to a high temperature, and the vaporized atoms or molecules are deposited on the substrate to form a thin film. Sputter deposition, on the other hand, uses ion bombardment to dislodge atoms or molecules from a target material, which are then deposited on the substrate. Ion plating is a combination of sputter deposition and evaporative processes.
Applications of Physical Vapor Deposition
The applications of PVD coatings are vast and varied. They are commonly used in the automotive industry for enhancing the durability of components, reducing friction, and providing decorative finishes. PVD coatings can improve the wear resistance of tools in the manufacturing industry, leading to longer tool life and increased productivity. The PVD process is also utilized in the aerospace industry to protect components from corrosion and wear in extreme environments. In the medical field, PVD coatings are used on surgical instruments to increase their lifespan and improve biocompatibility. Moreover, the electronics industry employs PVD coatings for manufacturing semiconductors, solar panels, and optical coatings on lenses and mirrors.
Differences Between CVD and PVD
Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) and PVD are both thin-film deposition techniques used in various industries. The primary difference between the two lies in the way the thin films are deposited. In CVD, a chemical reaction occurs at the surface of the substrate, leading to the deposition of a thin film. This process requires chemical precursors, which react at the substrate surface. On the other hand, in PVD, physical processes such as evaporation or sputtering are used to deposit the thin film, and there is no chemical reaction involved. Another key difference is seen in the type of materials that can be deposited. CVD is better suited for the deposition of high-performance materials, such as diamond-like coatings, due to the ability to control chemical reactions. In contrast, PVD is commonly used for depositing metals, such as aluminum or titanium, and compounds. Additionally, the temperature requirements for the two processes differ. CVD typically operates at higher temperatures to facilitate the chemical reactions, while PVD can be performed at lower temperatures.






























































